| | | |
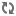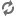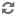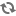 Uploading .... Uploading ....The Gothic link
The island of Gotland
... Wielbark Culture in the early 3rd century
Chernyakhov Culture, in the early 4th century
Roman EmpireIt is also related that because of overpopulation one third of the Gutar had to emigrate and settle in southern Europe. Some historians have argued[who?] that this tale might be a reminiscensce of the migration of the Goths.over a long time, the people descended from these three multiplied so much that the land couldn't support them all. Then they draw lots, and every third person was picked to leave, and they could keep everything they owned and take it with them, except for their land. ... they went up the river Dvina, up through Russia. They went so far that they came to the land of the Greeks. ... they settled there, and live there still, and still have something of our language.[citation needed]The name of the Gotlanders in Old West Norse is Gotar, which is same as that used for the Goths. Likewise the Old East Norse term for both Goths and Gotlanders seems to have been Gutar. Only the Goths and Gotlanders bear this name among all the Germanic tribes. The fact that the ethnonym is identical to Goth may be the reason why they are not mentioned as a special group until Jordanes' Getica, where they may be[citation needed] those who are called Vagoths (see Scandza). However Ptolemy mentions the Goutai as living in the south of the island of Skandia, who could be identical to the Gutar, since the "ou"-sound in Ancient Greek corresponds to the Latin and Germanic "u".Certain linguists[who?] point out that there are similarities between Gothic and Gutnish that are not found elsewhere in the Germanic languages. One example of this is the use of the word lamb for both young and adult sheep, which is only seen in Gutnish and Gothic.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/GutarSee more
Gotland is famous for its 94 medieval churches[10], most of which are restored and in active use. These churches exhibit two major styles of architecture:
Romanesque and Gothic.
The older churches were constructed in the Romanesque style from 1150–1250 A.D. The newer churches were constructed in the Gothic architectura...l style that prevailed from about 1250 to 1400 A.D. The oldest painting inside one of the churches on Gotland stretches as far back in time as the 12th Century.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/GotlandSee more
The Goths
(Gothic: 𐌲𐌿𐍄𐌰𐌽𐍃) were a heterogeneous East Germanic tribe, who played an important role in the history of the Roman Empire after they appeared on its lower Danube frontier in the third century.The first recorded incursion of Goths into the Roman Empire took place in 238. Written records about the Goths prior ...to this date are scarce, the most important source is Jordanes' 6th-century, semi-fictional Getica which describes a migration from Scandza, believed to be located somewhere in modern Götaland (Sweden), to Gothiscandza, which is believed to be the lower Vistula region in modern Pomerania (Poland), and from there to the coast of the Black Sea (Scythia, now Ukraine, Romania and Moldova). The Pomeranian Wielbark culture and the Chernyakhov culture northeast of the lower Danube are widely believed to be the archaeological traces of this migration.During the third and fourth centuries, the Goths were divided into at least two distinct groups, the Thervingi and the Greuthungi, separated by the Dniester River. They repeatedly attacked the Roman Empire during the Gothic War (376-382). In the late fourth century, the Huns invaded the Gothic region from the east. While many Goths were subdued and integrated into the Hunnic Empire, others were pushed towards the Roman Empire and converted to Arian Christianity by the half-Gothic missionary Wulfila, who devised a Gothic alphabet to translate the Bible.In the fifth and sixth centuries, the Goths separated into two tribes, the Visigoths and the Ostrogoths. Both established powerful successor states of the Western Roman Empire. In Italy the Ostrogothic Kingdom established by Theodoric the Great was defeated by the forces of the Eastern Roman Empire after the Gothic War (535–554). The fifth-century Visigothic Kingdom in Aquitaine was pushed to Hispania by the Franks in 507, converted to Catholicism by the late sixth century, and in the early eighth century fell to the Muslim Moors. While its influence continued to be felt in small ways in some west European states, the Gothic language and culture largely disappeared during the Middle Ages.
In the 16th century a small remnant of a Gothic dialect was described as surviving in the Crimea.[1]
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/GothsSee more
|
|
|
| | | |
|